Production Process and Characteristics of Tungsten Carbide
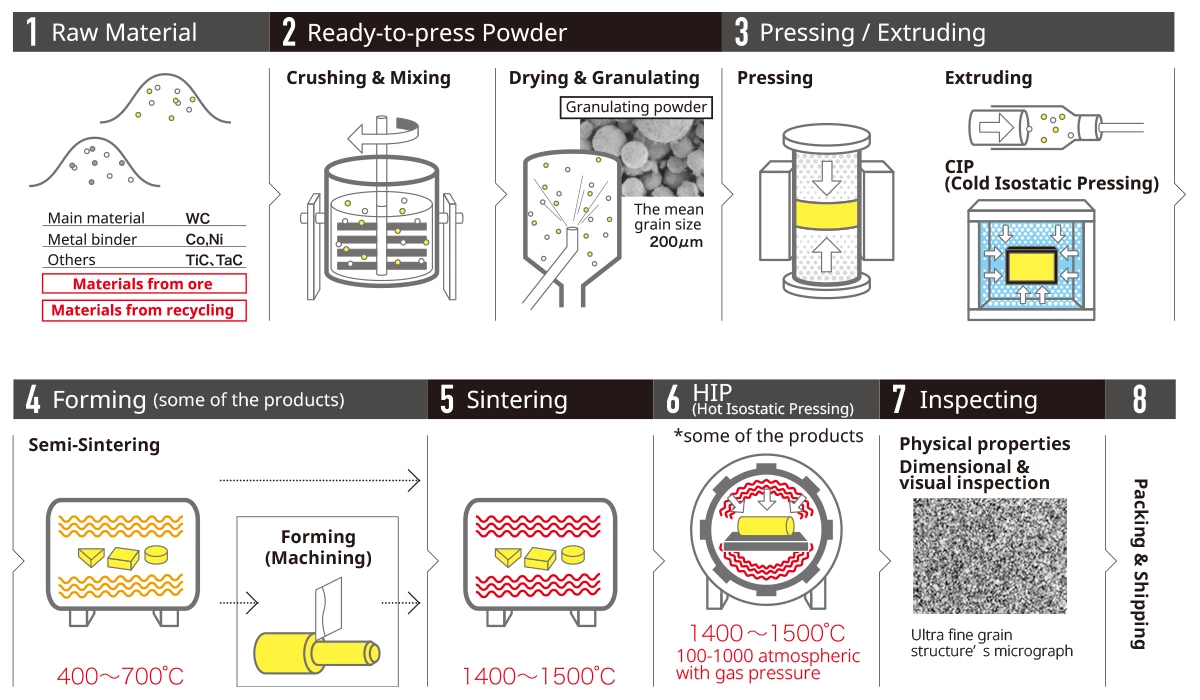
Production Process of Tungsten Carbide
Characteristics of Tungsten Carbide
Relation between Composition and Characteristics
Relation between Binder content and Hardness

The characteristic of carbide blanks (hardness & TRS) is effected by the amount of metal binder or grain size of tungsten carbide (WC).
Relation between Binder Content and T.R.S.*
*Transverse Rupture Strength

As Co content increases, hardness of carbide blanks decreases, but conversely, TRS increases. On the contrary, as Co content decreases, the hardness increases.
Relation between grain size of WC and hardness or TRS

By using smaller grain size of WC, carbide shows higher hardness and TRS, but fracture toughness becomes lower.
(Reference: “Relation between WC grain size and fracture toughness”)
Improvement of TRS by HIP

All of our carbide rods are treated by HIP to eliminate micro pore and improves TRS.
*HIP (Hot Isostatic Pressing)
(HIP is the process to treat carbide with high temperature and pressure.)
Relation between WC grain size and fracture toughness
Model of crack development
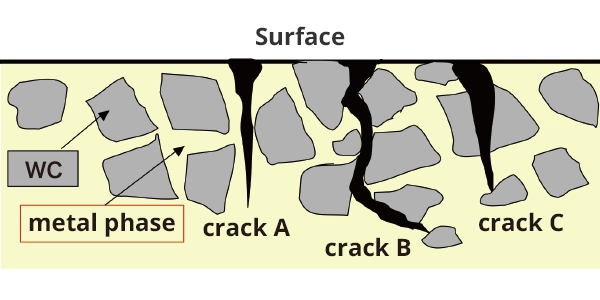
A : Crack development in binder phase
B : Crack development in binder phase –boundary surface of WC
C : Crack development in WC
 Fine grain
Fine grain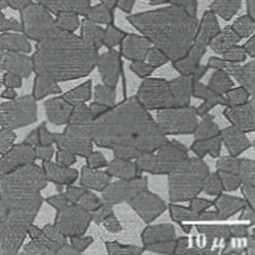 Coarse grain
Coarse grain

Carbide grade with coarse grain is effective for prevention of progress of cracks. It provide protection against chipping of cutting edges.
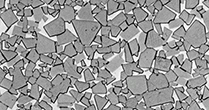
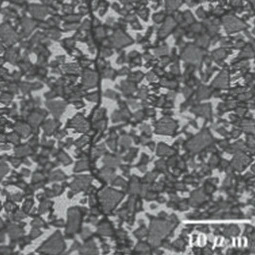
The microstructure by different WC grain
Carbide grades with ultra-micro grain or fine grain are commonly used for endmills and drills.
-
 Ultra micro grain
Ultra micro grain
-
 Micro grain
Micro grain
-
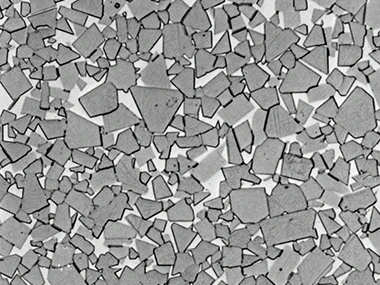 Fine grain
Fine grain
-
 Coarse grain
Coarse grain