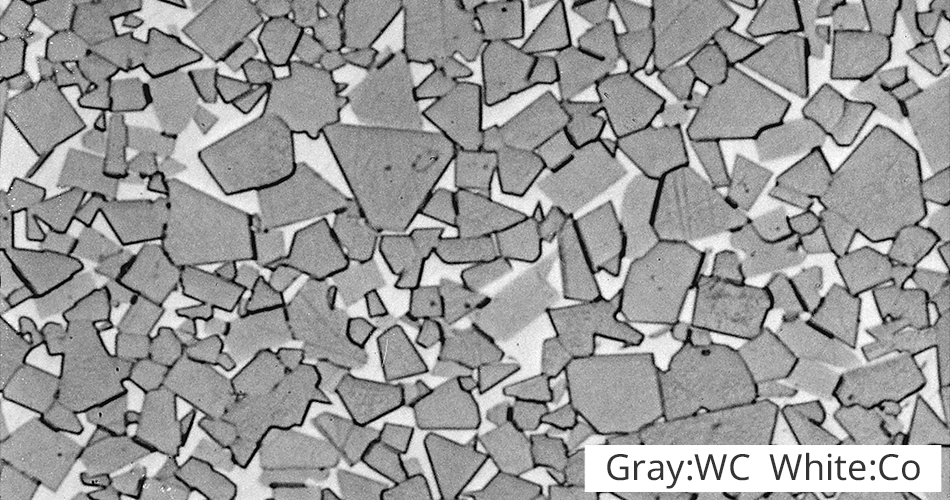
Swipe left or right
to see.
| High wear-resistance | High-hardness(Hv:15GPa) | 2 times(than high speed steel) | |
| Low elastic deformation | High Young's modulus(E:620GPa) | 3 times(than high speed steel) | |
| Low plastic deformation | High compressive strength(σ:5.3GPa) | 2 times(than high speed steel) | |
| Low thermal expansion coefficient | Linear expansion coefficient(α:5×10-6/K) | 1/2 times(than high speed steel) | |
| High thermal diffusion | High thermal conductivity(κ:80W/(m・K)) | 5 times(than high speed steel) | |
| High thermal transformation resistance | High heat resistance | ||
| High corrosion resistance | Possible to produce corrosion resistant alloy |